Introduction
Over time, cancer therapy has improved, giving millions of sufferers hope. This article discusses the latest cancer therapy treatments to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
I. Understanding Cancer
Before exploring cancer therapy options, you must grasp what cancer is and how it occurs. Cancer involves uncontrolled cell growth and division. Metastasis allows these aberrant cells to develop tumors, infiltrate neighboring tissues, and spread throughout the body.
- Cancer Causes
Genetic Factors: Mutations in several genes increase cancer risk.
Environmental Factors: Tobacco, UV light, and chemicals raise cancer risk.
Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, and alcohol can affect cancer risk.
II. Conventional Cancer Therapy Treatments
For decades, conventional cancer treatments have been the standard. These proven remedies have saved many lives.
- Surgery
Cancerous tumors and tissues are surgically removed. For localized tumors without metastases, it is generally the first treatment. Modern surgery, especially less invasive procedures, has improved patient outcomes and recuperation times.
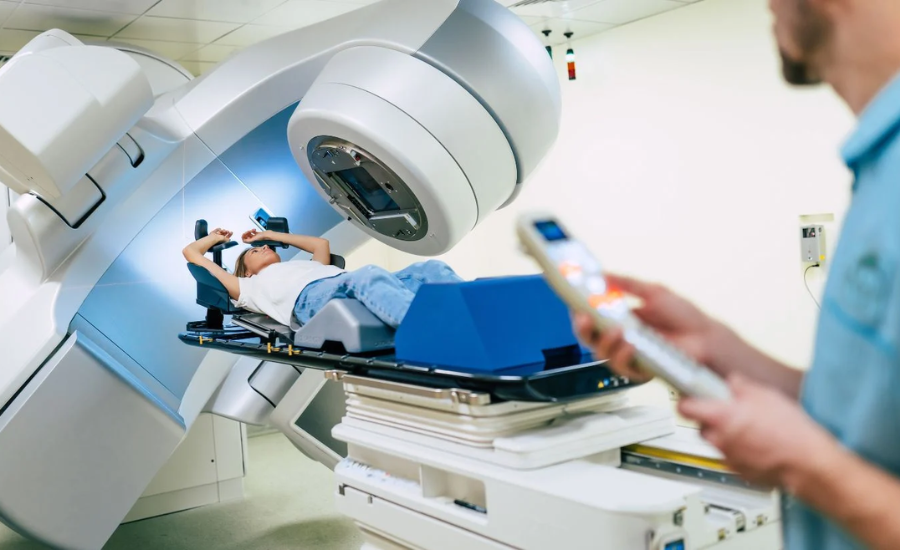
- Radiotherapy
Cancer cells are destroyed by high-energy radiation therapy. It can be used alone or with surgery or chemotherapy. Precision delivery systems like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) have improved radiation treatment while minimizing tissue harm.
- Chemotherapy
Drugs are used in chemotherapy to destroy or inhibit cancer cell growth. New medications and combination regimens have made chemotherapy more tolerable and effective, despite side effects like nausea and hair loss.
- Specialized Treatment
Targeted therapy drugs target cancer cell molecular or genetic defects. This method protects healthy cells and reduces negative effects. Targeted treatments have revolutionized breast and lung cancer treatment.
III. Immunotherapy: A Paradigm Shift
Immunotherapy revolutionizes cancer treatment. It detects and kills cancer cells using the immune system.
- Checkpoint Blockers
Immunotherapy medications called checkpoint inhibitors disable proteins that prevent the immune system from recognising and attacking cancer cells. Melanoma and lung cancer have been successfully treated with checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and nivolumab.
- CAR-T Cell Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T) is a revolutionary immunotherapy that genetically modified T cells to target cancer cells. Leukaemia and lymphoma have responded well to this personalized therapy.
- Immune Checkpoint Therapy Combinations
Clinical trials have demonstrated encouraging effects when checkpoint inhibitors are used with other immunotherapies. These combinations boost the immune system’s reaction to cancer cells, giving advanced or treatment-resistant cancer patients hope.
IV. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine customizes cancer treatment to an individual’s genetics and cancer-causing mutations. Effective therapy with fewer side effects is possible with this strategy.
- Genomic Analysis
Genomic profiling can now pinpoint a patient’s cancer-causing genetic changes. This information helps oncologists determine the best treatments.
- Liquid Biopsies
Blood or other physiological fluids are analyzed for cancer-specific biomarkers, DNA alterations, and circulating tumour cells in liquid biopsies. These non-invasive tests aid cancer diagnosis and therapy monitoring.
V. Emerging Therapies
New cancer medicines are discovered through research and clinical trials. These medicines are promising for cancer treatment but not yet generally available.
- Viruses that kill cancer
Genetically developed oncolytic viruses attack cancer cells without harming healthy cells. Novel cancer therapies using these viruses are being explored.
- Nanotech
To minimize tissue harm, nanotechnology delivers medications directly to cancer cells utilizing tiny particles or materials. This strategy may improve therapeutic efficacy and reduce negative effects.
- RNA treatments
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) therapies are being studied to target and block cancer growing genes.
VI. Supportive Care and Survivorship
disease therapy should improve patients’ quality of life and address their physical and mental issues in addition to curing disease.
- Hospice Care
Palliative care relieves cancer therapy side effects such pain, tiredness, and nausea. It can be given with curative therapy to increase patient well-being.
- Care for Survivors
As more people beat cancer, survivorship care is crucial. Cancer survivors’ long-term physical, emotional, and psychosocial needs are addressed in this treatment.
VII. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Cancer treatments advances are promising, but they also present ethical issues.
- Price and Access
Access to cutting-edge cancer treatments may be limited and expensive, prompting problems about equity and affordability.
- Moral Problems
Patients, families, and healthcare practitioners may face ethical problems while choosing experimental treatments, end-of-life care, and genetic testing.
VIII. Conclusion
Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, precision medicine, and new medicines have advanced cancer treatment. These advances give cancer patients and their families hope, boosting survival and quality of life during and after treatment.
Oncology must prioritize patient-centered care, solve cost and access issues, and handle ethical issues as it evolves. We can make cancer a manageable chronic illness and cure with continued study and collaboration.